By Anne Nagro, Contributor April 21, 2020
An ISP, or internet service provider, is a company that lets you access the internet from home, usually with a monthly subscription. Think of it like a cable company, but instead of connecting you with TV channels, an ISP connects you to the internet.
An ISP may sell one or more types of internet service, also called connection types. The most common types are cable, fiber, DSL (Digital Subscriber Line), and satellite internet.
High-speed internet service is caiied broadband. Non-broadband internet is slower. According to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), a connection must deliver download speeds of at least 25 megabits per second (Mbps) and upload speeds at a mininum of 3 Mbps to be considered as highspeed. The types and levels of online activities your household enjoys determines the connection speed you need.
According to Leichtman Research Group, which analyzes the broadband industry, 85% of U.S. households subscribe to an internet service. We’re also spending more time online. American adults with home internet access spent 3. 7 hours a day online in 2019, compared to 2.8 hours in 2014, reported the same study. Much of this is spent watching videos, with half of all households watched video online daily, up from 29% in 2014, the company found.
When it comes to choosing an internet provider, most of us have a choice. The FCC says 94% of Americans have three or more ISPs offering broadband internet where they live. However, not all types of broadband are available in all areas. Rural and outer-suburban areas in particular have more limited options.
Types of Internet Service
Internet service providers use different technologies to connect you to the internet. Some may use more than one to complete the “last-mile” connection,which is the distance from the junction box or ISP facility to your door. Types of internet connections include:
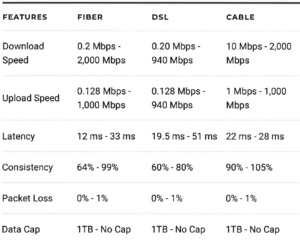
Cable Internet: This service uses coaxial cable. It’s the same cable that delivers cable television to a home, and providers of cable TV generally also sell cable internet service. Cable internet is fast and reliable, consistently delivering advertised speeds. It also has low latency, which means users experience fewer delays or lag time, such as when playing online games.
Cable internet is widely available and is often consumers’ top pick for internet service. In its most recent report on internet access, the FCC says 382 companies offered cable internet service in 2017. The top cable companies have about 68 million broadband subscribers, states Leichtman Research Group. For more information, see our rating of the Best Cable Internet Providers in 2020.
Fiber Internet: This service uses fiber optic cable made from strands of glass to transmit data at the speed of light. As such, fiber internet has some of the fastest download and upload speeds. It also has the lowest latency of internet technologies, which translates to fewer delays for gamers and video conferences. Fiber supports heavy internet use. Multiple users can simultaneously stream video, play live-action games, and share large files, as well as connect numerous personal and household devices.
Fiber broadband is available to about 39% of the U.S. population, reports the FCC. Nonetheless, the network is growing, with fiber deployed to a record 5. 9 million homes in 2018. And adding fiber broadband access increases rental and property values, accoiding to a study conducted for the Fiber Broadband Association. For more information, see our rating of the Best Fiber Internet Providers in 2020.
DSL: Digital Subscriber Line ( DSL) connects you to the internet using the telephone line. Since most homes are wired for telephone, the service is widely available and traditional telephone companies typically offer DSL. Almost 88% of people in the U.S. have access, says the FCC. However, even when high-speed DSL internet access is available in your area, keep in mind that the farther you live from the ISP’s facility, the slower the speed. Distance increases line interference and weakens the connection.
In general, DSL internet is faster than satellite internet but not as fast as cable and fiber internet. For more information, see our rating of the Best DSL Internet Providers in 2020.
Satellite Internet: This wireless internet service uses geostationary satellites to send and receive data between your home and the internet. But because data has to travel to space and back, it has the highest latency, or delay, of all connection types. Additionally, its internet speed can be affected by weather and how busy the network is at any given time. Data caps that limit your total data usage are common. The combination of these drawbacks makes satellite internet a poor choice for real-time gameplay or binge-watching online videos.
That said, satellite internet is often one of the only high-speed options for people living in rural areas and places served by slower dial-up, DSL, or mobile internet plans. Satellite internet is accessible to nearly the entire U.S. population, reports the FCC. For more information, see our rating of the Best Satellite Internet Providers in 2020.
Dial-Up Internet: Around since the 1990s, dial-up uses your existing phone line to make an internet connection. It is not “always on” like broadband internet service. Connecting to the internet requires dialing an access number (which looks like a phone number) and using a special modem. Unlike with a DSL connection, you cannot make phone calls while online when using dial-up.
With dial-up, the maximum speed at which you can send and receive data is 56 kbps, which may cause some applications and webpages to time-out before loading. Dial-up access is low cost, accessible (most homes have a landline), and secure. It may be one of the few internet options in rural areas.
Most people have switched to faster technologies. In 2015, 3% of Americans were using a dial-up connection, according to the Pew Research Center.

